How to Develop an App Like Swiggy? Tips from Swiggy App Developers

Safety rules during the COVID-19 pandemic period made on-demand food delivery applications even more popular. Statista’s study finds that around 44% of consumers in the US use food delivery services at least once per month. It’s a great time for online food startups to succeed, isn’t it?
Although global players like UberEats and Swiggy lead competitors in the market share of food delivery orders, it is still possible to develop a global food delivery marketplace by learning from their mistakes. Or you can try creating a Swiggy-like food delivery app for uncovered regions and then sell your business to global players.
It’s not easy to build an app like Swiggy. The development takes time, money, and planning—you won’t fit all the features in a single app.
Let’s find out how a food delivery marketplace like Swiggy operates and how much it will cost you to build a food delivery app.
Here’s What We’ll Cover
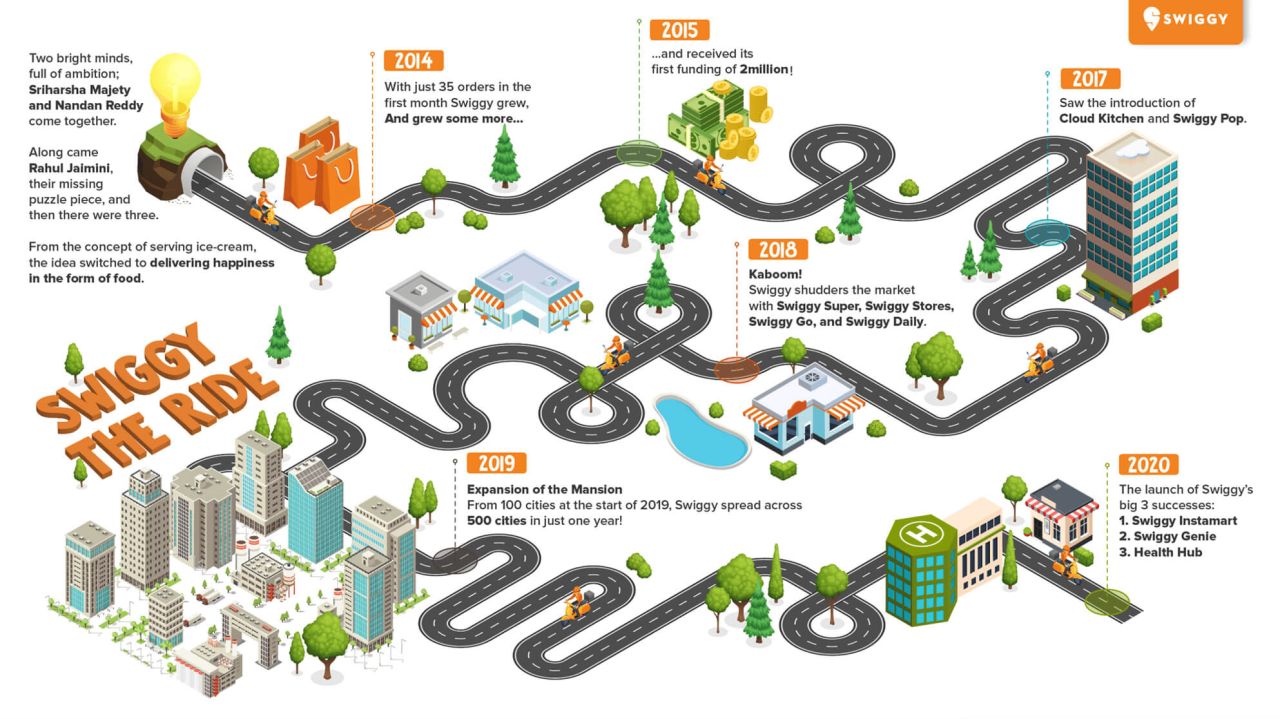
How Swiggy Became a Unicorn Startup
The Swiggy Story
Swiggy started in August 2014 as an online food ordering and delivery startup.
In 2019, Swiggy launched the instant pickup service Swiggy Go, which is used for a diverse array of items, including laundry, document, and parcel deliveries to business clients and retail customers.
In 2020, the company launched its grocery delivery platform called InstaMart.
Later, Swiggy and ANRA Technologies joined hands to introduce drone delivery trials in India.
Today, Swiggy is India’s largest online food ordering and delivery platform, that can boast over 5,000,000 mobile app installations. It has 125,000 restaurant partners countrywide and hired more than 5000 employees across the country. Our success may look instantaneous, but actually, it is a result of meticulous work, many trials, even more errors, and yet, still more corrected errors that led to success.
Swiggy Business Model: How Does Swiggy Work?
The business model of Swiggy is based on hyper-local on-demand food delivery services. Users can order food from any eating venue listed on the Swiggy app. Note, that Swiggy’s fleet services both delivery and delivery partners, and it can pick up and deliver food in less than half an hour. Swiggy’s business model is based on a dual-partnership model.
Its key partners are:
- Restaurant partners
- Delivery partners
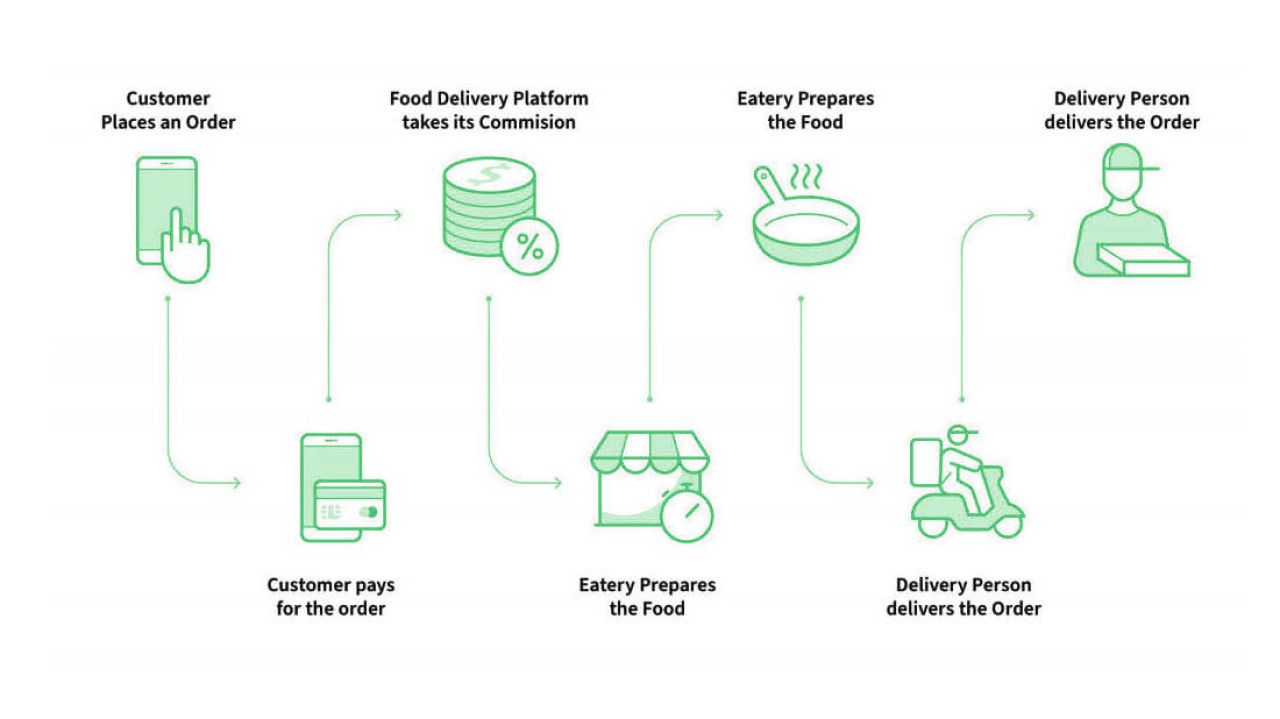
Swiggy’s working process involves four main steps:
- Search. Customers enter their location in the Swiggy app. Then Swiggy shows popular food and eating venues in and around that area.
- Place an Order. After the customers choose what they want to order, they complete the transaction by making an online payment or opt for cash.
- Process. Swiggy directs the order to the respective restaurants. The restaurants prepare and pack the order for delivery.
- Delivery. Swiggy delivery personnel pick up the order from the respective restaurant and deliver it to the customer.
More information can be found in the table below.
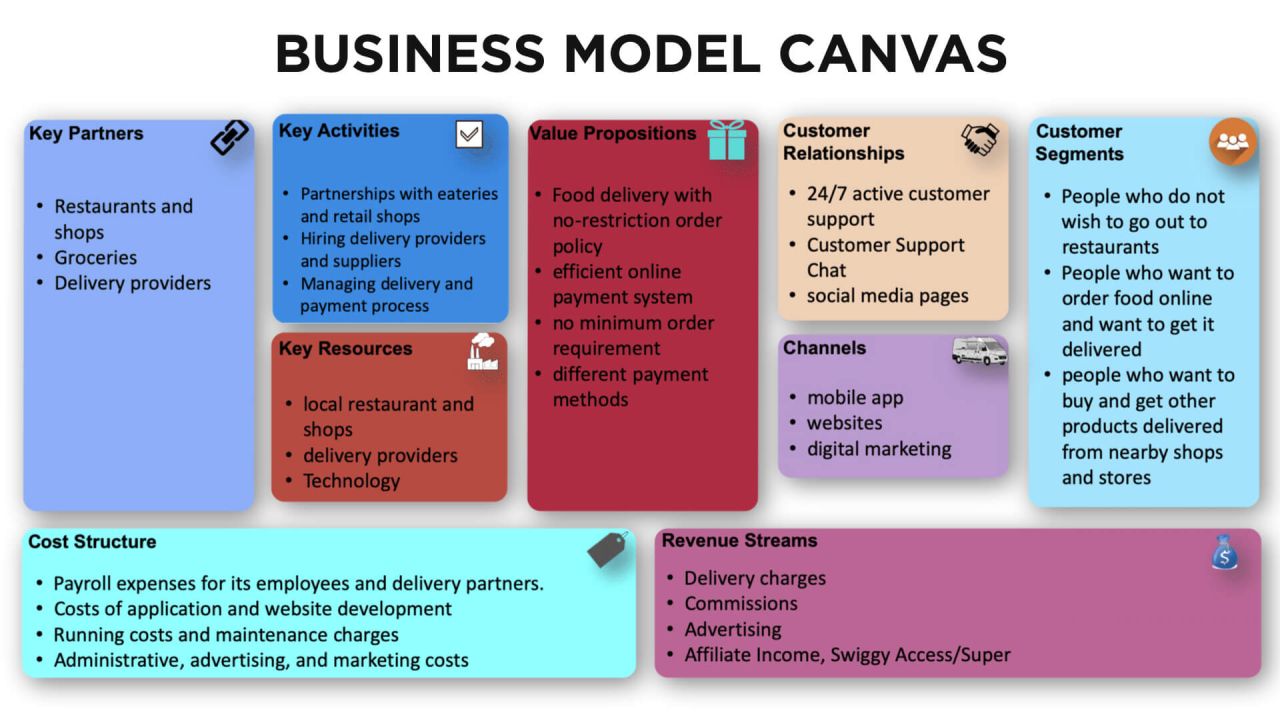
The main factors that play an essential role in determining the cost structure of the Swiggy business model are:
- Salaries of staff and distribution partners
- Maintenance and operating costs of the Swiggy business model
- Developing apps, websites, and other costs associated with the business framework
- Advertising, marketing, and administration costs.
How to Make a Food Delivery Application like Swiggy: Steps to Follow
Choose Food Delivery App Model
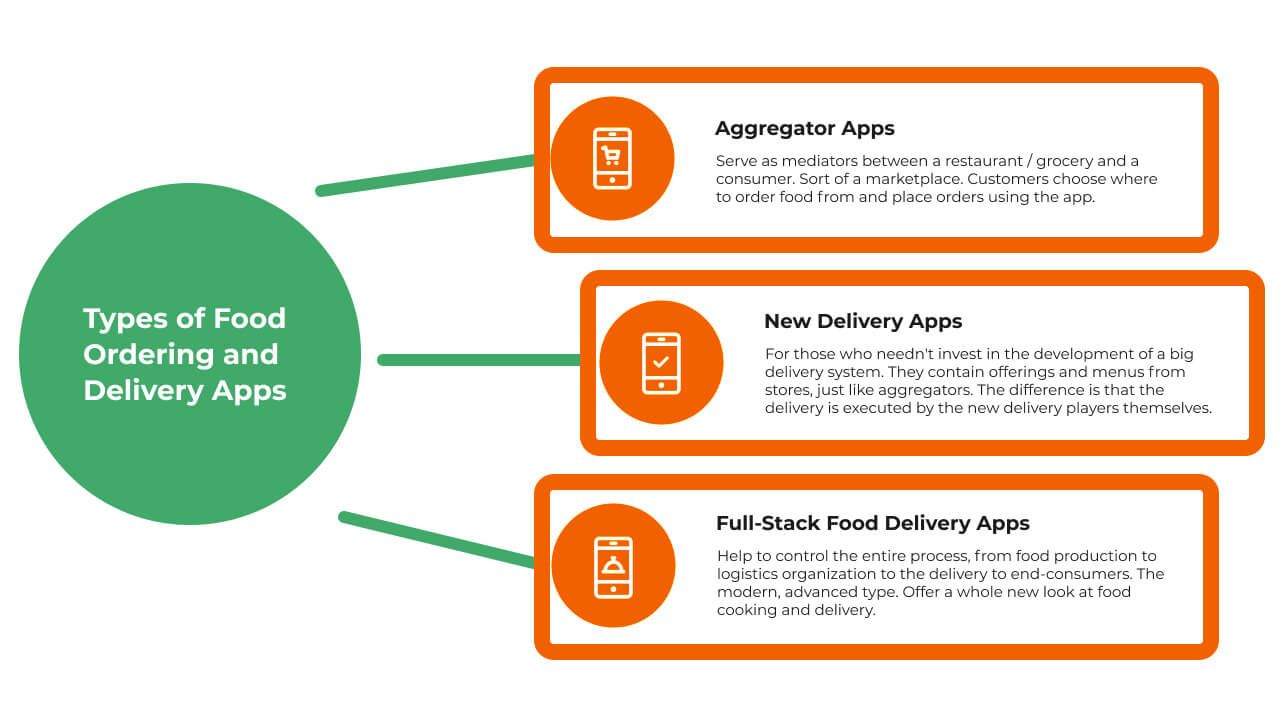
All the food delivery apps provide quick, online access to menus and discounts, offer convenient payment options, and feature real-time delivery tracking. However, app models such as aggregators, new delivery apps, and full-stack apps are designed for different purposes.
Category 1. Aggregators or Order-focused Food Delivery Services
The aggregator model allows users to access one portal and order from their favorite restaurants, receiving their favorite dishes. The disadvantage of this model is that the restaurant is also responsible for delivering the food; therefore, it takes more time for the dish to get from the cook to the customer. The app owner only provides order processing; the restaurant is responsible for cooking and delivery.
Examples of food delivery startups working under this model are Just Eat, Hero, GrubHub and Foodpanda.
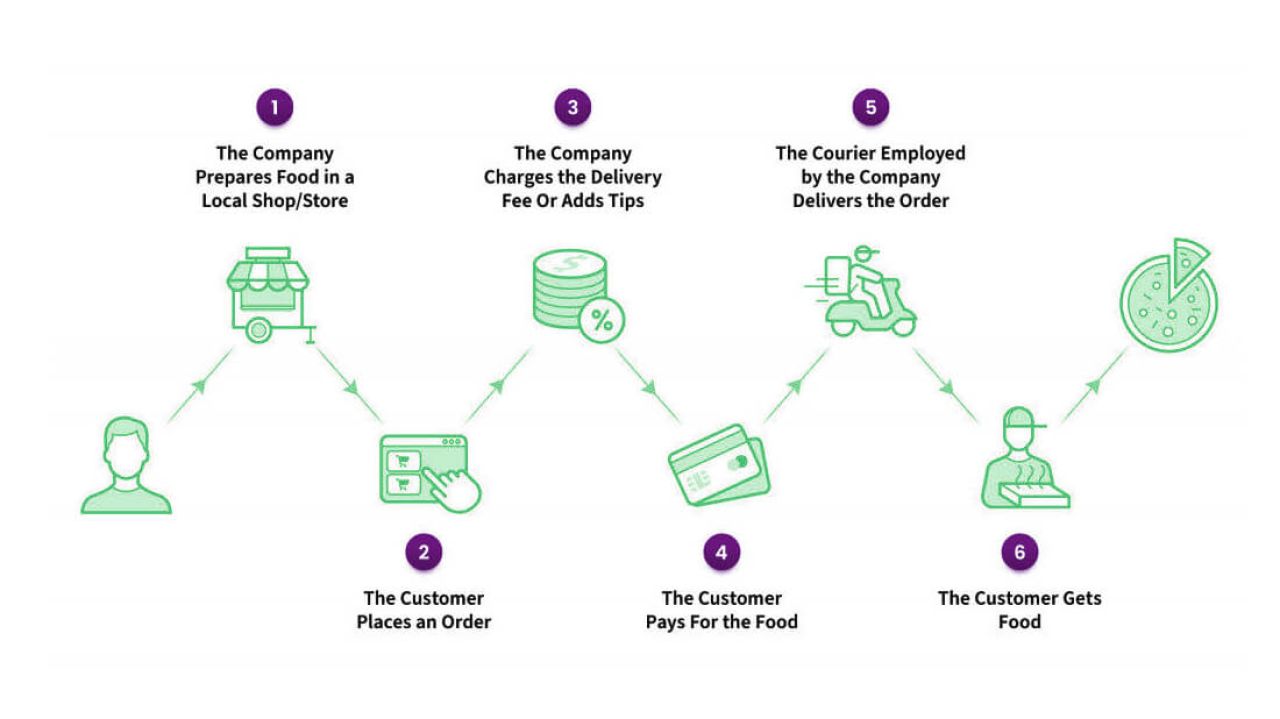
Category 2. ‘New Delivery’ or Logistics-focused Platforms
The new delivery app is responsible for food distribution in addition to helping the restaurant manage the orders. The orders come to the administrator, who allocates them between couriers and sends a request to the restaurant kitchen to cook the dish. These delivery and order apps are beneficial for new restaurant promotions and restaurants without delivery services. It costs more to cooperate in this way; however, only a few restaurants have a delivery system in place, so services such as the new delivery apps are a great opportunity for restaurants to dedicate their time to cooking.
Bright examples of the projects belonging to this category are Uber Eats and Postmates. Swiggy also follows this model of delivery.
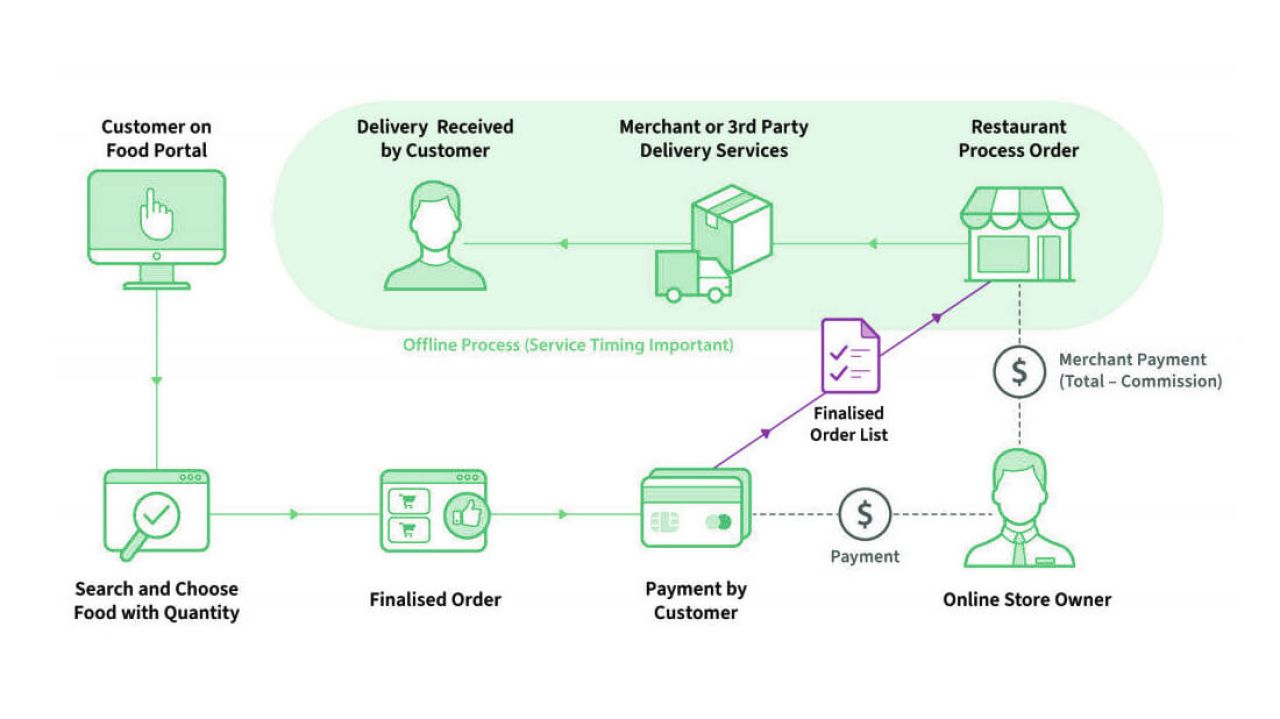
Category 3. Full-stack Delivery Services
The full-stack delivery services run the entire process, from cooking to receiving payment. This system’s integration requires a lot of time because such services are usually divided into three interconnected apps: one for the courier, another for the restaurant, and yet another for the consumer. This design helps to meet the needs of all parties. At the start of the process, the order moves automatically from the customer to the restaurant. The manager is notified about the new request, and the kitchen starts cooking immediately. When the meal is ready, the restaurant ensures that the order is visible to the couriers waiting nearby. The courier chooses what to deliver and ends the cycle by arriving at the consumer’s door.
Some examples are Fritchti (France) and Munchery (USA).
| Aggregators or order-focused food delivery services | ‘New delivery’ or logistics-focused platforms | Full-stack delivery services vs. order- and logistics-focused platforms | |
| Companies | Delivery.com
Eat24 JustEat |
Swiggy Deliveroo Doordash UberEats |
Fritchti Munchery |
| Description |
Companies only manage orders. |
Food startups are responsible for both managing orders and delivery. |
Companies run the customer interaction management, cooking and logistics. |
| Monetization |
Commissions Featured restaurants |
Commission Delivery fee |
Service charges Profit generation Special packages |
| Limitations |
Meal options are limited in this model. You can only list those items that the restaurants can prepare. You cannot charge a higher price than what the restaurants charge. No control over the food quality and custom services. |
You need to hire and train employees. The increased amount of management work may impact business scaling. |
The end-user is usually attached to a restaurant name and tends to order from their favorite eatery. The startup cost of this business model is higher. Managing the whole network of operations is complex. Inefficiency in any aspect can lead to low-quality service. |
| Benefits |
This model is easy to start and has a lower capital requirement. No hassles of delivering or preparing the snacks or meals. Easy to scale and grow, as you only need to add more restaurants to your app. |
Once such a food delivery system is in place, you will develop a company and receive a profit. |
The combination of food delivery with other aspects makes this model preferred by investors. You will have complete control over the entire supply chain of the orders. No dine-in means the setup cost of a restaurant will be much less. |
Key Features of a Successful Food Delivery App
If you’ve decided to go digital and create your own Swiggy clone app, the first thing you should pay attention to is the set of features your app should have. Based on our experience, we would recommend you to consider adding the following:
- Customer panel
- Restaurant panel
- Delivery person panel
| Customer app features | Restaurant panel features | Delivery person app features |
|
Registration and login processes will differ; users can use email registration, registration via social media, or personal login and password. |
Registration and profile management feature works the same way as with customers and couriers. Food venues should be able to add business details to their profiles. |
Registration and profile features allow couriers to access the system with their credentials. |
|
Search field. After profile setup, users get access to the catalog of venues. Offer filters that allow sorting options by price ranges, cuisines, or ingredients. |
Content management. Restaurant staff should be able to add and update details about the eating venue, including its name, address, working hours, etc. Restaurant staff should be able to update the menu and add photos to attract users. |
Order management. Couriers can access all relevant data, including the list of the nearest orders. To start accepting offers, couriers toggle a “go online” button. Couriers can both accept and decline customer requests. |
|
Order placement. The order placement process should be clear and easy. A complicated process might lose customers before getting any income. Users should have the ability to add a dish to their carts, edit the order or remove it in a few clicks. |
Order management. The employees should track incoming orders and update order statuses in real time. |
Status updates. For customers’ convenience, delivery personnel should update their status along the way. This feature allows clients to be aware of order processing and estimate the waiting time. |
|
Payments should be processed with speed, security, and convenience. Consider integrating a few payment gateways like PayPal or Stripe. |
Payments feature allows accessing, managing, and fix the payment options and gateways for accepting or sending payments online. |
Delivery history feature allows couriers to leave a note about difficult delivery places or routes. |
|
Order tracking. The tracking feature helps users find out when the order will reach them. The courier tracking is done with a Location API. |
Metrics. For delivery app development, it’s essential to implement features for collecting and analyzing metrics. For your convenience and dynamic visualization, the data can be presented as infographics instead of simple tables. |
Earnings screen feature enables couriers to check their daily and monthly earnings. |
|
Notifications. Notification about order status (Placed, In Progress, On Its Way, Delivered) via push notifications works perfectly. Ensure sure only essential data is sent. |
Courier management. In addition to your partners’ information and the ordering flow management, you’ll need to guide your couriers and track their performance. |
Maps & navigators. To save couriers’ time, you can implement a map and navigator into the on-demand delivery app. Some navigator apps are tailored for certain means of transport. |
|
Ratings and reviews allow users to rate restaurants. |
Calendar. Normally, such a delivery service doesn’t have a fixed working schedule. You can organize the workflow so that couriers can book their working time in advance via the calendar. |
Add More Features to Win More Users
The features we’ve listed above are required to build an app like Swiggy. To enhance the UX, make your app stand out, and win more users, you may think of applying additional features.
They may include:
- Bookmarks allow foodies to mark dishes they want to try or add the best eating venues to order from.
- Order history allows users to check the order history, easily find the dishes they like most, and order them again.
- Estimated delivery time allows customers to plan their time better without waiting and guessing.
- Discount system. Start with free delivery services or a free drink for big orders to boost customer loyalty. You could also adopt membership or cumulative discounts or special promo codes.
- Social networks. By allowing users to link their social network accounts, you can boost their loyalty and promote your business.
- Chatbots. Moving from their earlier preference for phone support, more than 75% of Swiggy’s user base now rely on chat for quicker resolution of issues. For example, Swiggy’s order experience is very transparent, thanks to its live tracking.
- Groceries and genie. Those two services were added to Swiggy Business Model during COVID-19. Swiggy Genie allows ordering necessities such as home-cooked meals, medicines, test reports and groceries to be delivered to the doorstep. This feature has led to increased revenue.
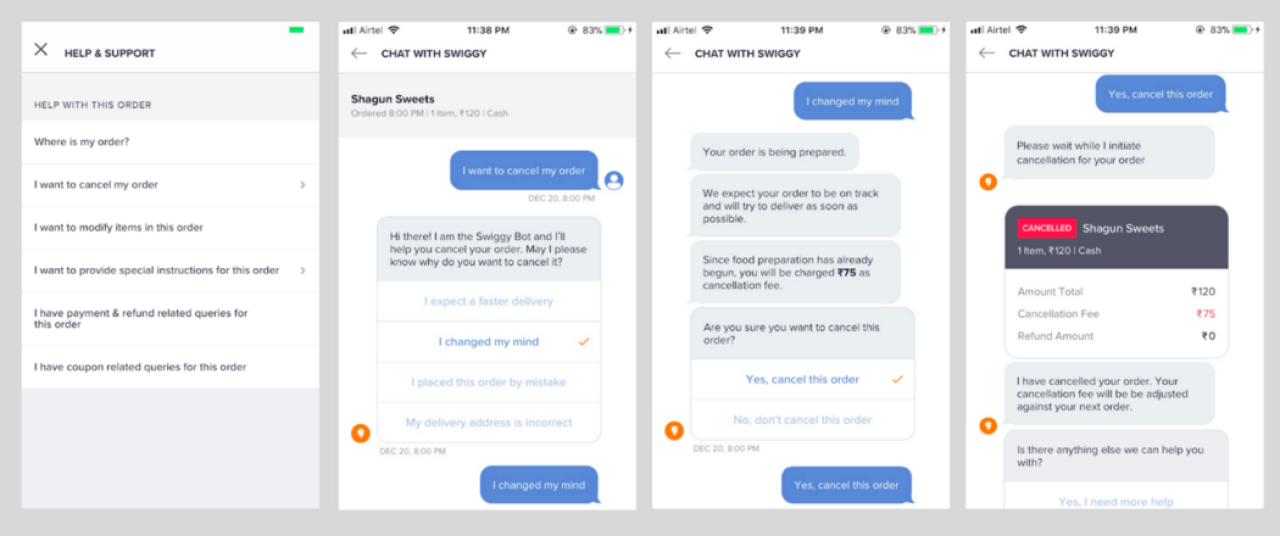
Cancelling an order via the chatbot
Select the Technology Stack of Food Delivery App Development
We’re not going to cover all the steps it would take to build a food delivery app like Swiggy here because that would be too long. Instead, we will describe the tools and technologies that can be used to create a Swiggy app clone.
- Programming languages: Kotlin (Android), Swift (iOS).
- Back-end development: Node.js
- Data platform: S3, Presto, Druid, Snowflake, Flume, Hive, Spark, Storm
- Database: Postgress, HBase, MongoDB, Cassandra
- Data storage: Amazon (AWS), Microsoft (Azure), and Google.
- Navigation: Google Maps. Google Directions
- Push notifications: Push.io, Twilio
- Addresses: Google Places
- Analytics: Storm, Flink, Firebase.
- Cloud environment: Azure, Google, AWS.
- User login: Facebook/Google Software Development Kits (SDK)
- Restaurant listings: APIs (e.g., GrubHub or FourSquare).
- Secure payments: Google Pay, Amazon Pay, Stripe, iOS Wallet, Netbanking, PayPal, Braintree.
- Mailing service: Amazon SES
- SMS service: Twilio
- Synchronization: Socket.io
- Chatbot: natural language processing (NLP), Java, Node JS, Ruby on Rails, Apache Kafka, MySQL, Postgres, Redis, React.
This list of technologies may differ from app to app according to your business objectives, features, and platforms.
Swiggy’s Revenue Model: How Does Swiggy Make Money?
How do free apps like Swiggy make money? In recent times, we have heard many questions about the hottest topic on the app market. It’s time to reveal the truth behind app monetization magic.
Advertisements
Advertising is a core money-spinner. It generates revenue in two ways:
- Priority listing of restaurants. Swiggy has a list of restaurants on the main screen. Restaurants pay for a higher listing in the search results.
- Banner promotions. Swiggy charges restaurants to display their banner ad.
Delivery Charges
This type of income Swiggy generates from customers. All orders below Rs.250 are subject to a delivery fee. The amount of delivery charges depends on the delivery distance, order demand, and weather conditions.
Affiliate Revenue
Swiggy has collaborated with several financial institutions to give special offers to customers who purchase and use the credit cards of these banks.
Fixed Commission
Swiggy charges a commission from restaurants to generate sales and deliver food through its fleet. This commission depends on the value of the restaurant’s order, location and popularity. It varies from 15% to 25%.
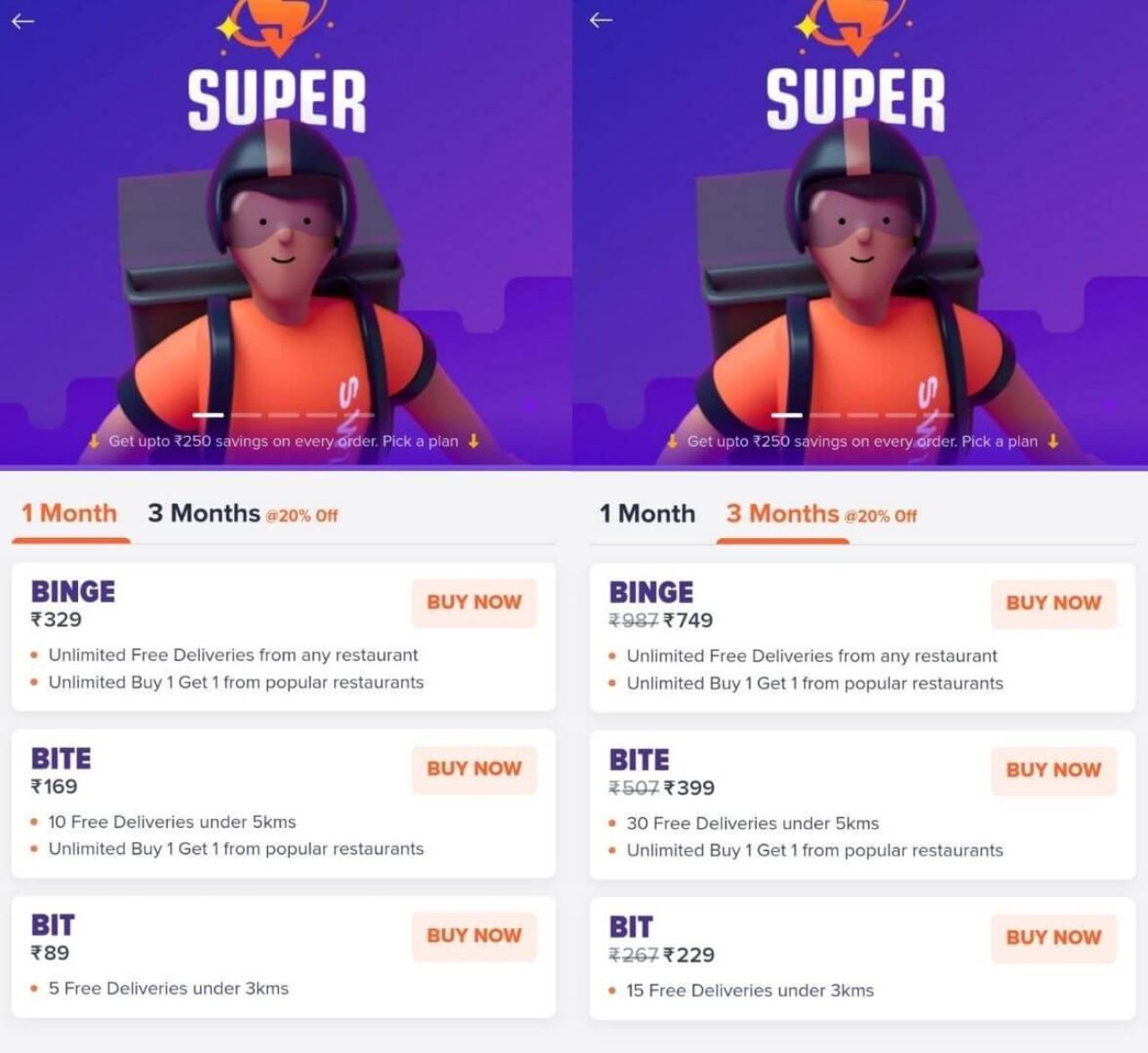
Super Swiggy
Super Swiggy membership program members do not have to pay delivery charges on orders above Rs.99. Also, they do not need to pay an extra fee.
Track Popular On-demand Food Delivery Apps
Creating a food delivery app to improve your business is a good idea, especially given the achievements of other popular apps.
Uber Eats

Uber Eats is a food delivery service that’s an offshoot of the Uber ride-hailing service. You can place orders with local restaurants from the Uber Eats website or mobile app, and food is delivered directly to your door, usually for a small delivery fee. The app allows you to set up group orders or schedule orders for a later time as well.
Postmates

Postmates is a delivery app that allows you to order food from your phone and have it delivered to your door. Postmates isn’t only for food delivery. In addition to takeout, you can order delivery from certain grocery stores, pharmacies, and even electronics and liquor stores, depending on where you live and which nearby stores are available.
Note Postmates is a tad more expensive than other delivery apps. On top of a delivery charge that can run between $3.99 and $5.99, they also charge a 9% service fee.
Deliveroo

Deliveroo is an online food delivery service that allows you to order food from restaurants near you. You can order food through their website or mobile apps on Android and iOS. Deliveries are executed by contractual drivers who operate on an on-demand basis. One of the major differentiators to other food delivery companies is the focus on high-quality food offerings.
Deliveroo makes money via delivery, sign-up and service fees, and by offering premium subscriptions and selling food through its cloud kitchens.
Grubhub

Grubhub is an online and mobile food-ordering and delivery marketplace with nearly 24 million active diners. Let’s take a look at some of the features that explain its enduring influence:
- Appeared rather early and had no alternatives
- Works with almost every restaurant in a city
- Offers coupons for some restaurants
- Users can rate restaurants to let future diners know whether they are worth ordering from
- Shows the average price of the dishes at the restaurants
- Estimates of delivery time based on your location
DoorDash

DoorDash app provides restaurant food delivery services. DoorDash now boasts operations in 4,000 cities across North America and Australia. Featuring a wide range of cuisines from sushi to fast food, DoorDash features easy ordering, with options to track your delivery, pick up your food or schedule your deliveries for the most convenient times.
DoorDash also lets you order alcohol and mixers from local wine and liquor stores where local laws allow. And as with other best food delivery services, delivery instructions in DoorDash enable you to specify where you’d like your meal dropped off for contact-free delivery.
How Much Does It Cost to Develop a Food Delivery App Like Swiggy?
We scoped out a Swiggy minimum viable product (MVP) to see how much it would cost to outsource its development. A Swiggy clone can cost from $150k for basic applications with limited features to $250k–$350k for a multi-platform app with advanced features.
| Customer’s MVP | ||
| Feature | iOS | Android |
| Back-end | $7670 | $7670 |
| Front-end | $20,490 | $15,690 |
| Design | $2500 | $2500 |
| Project Management | $5150 | $5150 |
| Quality Assurance | $7700 | $7700 |
| Total | $43,510 | $38,710 |
| Courier’s MVP | ||
| Feature | iOS | Android |
| Back-end | $13,500 | $13,500 |
| Front-end | $5835 | $6300 |
| Design | $2000 | $2000 |
| Project Management | $2575 | $2575 |
| Quality Assurance | $5125 | $5125 |
| Total | $29,035 | $29,500 |
| Restaurant MVP | |
| Feature | Price |
| Back-end | $5700 |
| Front-end | $4740 |
| Project Management | $1044 |
| Quality Assurance | $2088 |
| Total | $13572 |
Consider Launching a Food Delivery App?
Now, let’s summarize what we’ve covered in this article.
- There are three types of delivery app business models—aggregators, new delivery apps, and full-stack apps.
- When setting up the delivery, decide how you’ll cover delivery costs.
- You’ll most likely need three versions of your platform—for customers, couriers and an admin panel.
- Decide on what features you’d like to have on your platform.
- To start the development process, find a trusted software development company that will assist you all the way through.
If you need some help with the development or have any questions left, feel free to drop us a line.




