How Healthcare Mobile Apps Are Changing The Industry

But today, over a million people get rid of excess weight this way.
It is hard to believe that something that sounded like a fairy tale a few decades ago would become a part of everyday life. However, it is happening, and it is all due to the development of mobile technologies.
According to Statista, today about 3.2 billion people have a smartphone, and by 2021 the figure will increase to 3.8 billion.
The Ericsson Mobility Report also expects the 5G technology to have 2.6 billion subscriptions covering up to 65 percent of the world’s population by 2025.
The more common mobile phones become, the more common mobile applications become. And the healthcare industry is one place where mobile technology is making its mark.

The State of Mobile in the Healthcare Industry Today
The Mobile Health Market Report projects a global market evaluation of 21.71 billion by 2023 and 36.5% CAGR during the forecast period of 2017-2023.
The forecasts show that smartphones and healthcare are becoming more closely integrated. Revenues in the market for applications providing health services are constantly growing.
In 2017, the number of medical mobile applications already exceeded 325,000, according to R2G mHealth Economics research.
The health sector has become very attractive to such giants as Google and Apple. In addition to their investments, they have developed their own medical applications, such as Apple’s HealthKit and Google Fit.
All of this interest shows how important mobile applications in healthcare are becoming to consumers, doctors, and enterprises.
Types of Mobile Apps in the Healthcare Industry
We can divide healthcare mobile apps into three types:
- Those designed for healthcare providers.
- Those designed for patients.
- Those designed for the general public.
The first type is mainly intended to help physicians rapidly and effectively work with large volumes of medical data.
This area also includes applications that allow doctors to receive advice from their colleagues: for example, specialists with particularly difficult cases can use healthcare mobile apps to seek help from the medical community.
Figure 1, sometimes called “Instagram for doctors,” is a good example of an app developed to let experts connect with each other. Doctors can share photos related to different medical cases and discuss them. (Naturally, photos are only published with the patient’s consent.)
Follow the link to see more apps of this type, developed by our company: Trauma Anatomy, VR ECG Simulator, CephX, AnatomyNext all of them aim to help doctors with their work.
Applications of the second type are used to monitor patients’ health parameters, and to allow patients to communicate with their physicians.
For example, the AmWell app allows patients and doctors to connect remotely. It includes such features as a virtual waiting room, e-prescribing, payment collection and more. Communication with doctors via video is also available, enabling physicians to make diagnoses and, if necessary, prescribe medication.
The other example is Livia. This app is a whole platform with a large functionality like ordering medicine at best prices from different pharmacies, booking a visit to a doctor, having direct access to patients for chemists.
The third type is focused on the overall improvement of people’s health. These are the applications that let you track weight gain or loss, or manage your diet. They are sometimes called “apps for healthy living.”
Check out our All-in Fitness App. Our challenge was to develop an all-in-one fitness app to complement the training of fitness enthusiasts at any level.

Zombies, Run! is a very unusual example of this type of app. You put on your headphones, go for a run and, when you hear the sound of approaching zombies, speed up to make your escape. As you progress, you can gather supplies and build a base to defend yourself.
The game’s makers claim that it is the most popular fitness app, used by one million players worldwide.
The Three Main Ways That Healthcare Mobile Apps Influence The Industry
Here are some examples of the changes that applications are bringing to healthcare.
1. Healthcare Mobile apps provide access to healthcare for low-income patients.
According to Kaiser Family Foundation data, in 2018, 27.9 million nonelderly individuals in the US were uninsured (an increase of nearly 500,000 from 2017). These people didn’t have access to affordable, reliable, quality medical care.
Mobile phones are now available to almost everyone, service is not very expensive, and many people already have a service plan anyway. This makes medical apps a potential benefit for certain segments of the population.
Katie Dupere, a Social Good reporter at Mashable, revealed the scale of the savings with the AmWell application, “Physicians cost $49 or less to chat with — significantly less than the $160 an in-office visit costs the average uninsured patient.”
2. Mobile technology improves physicians’ workflow.
Medical applications help physicians optimize work, allowing more time to be given to the treatment of patients.
Healthcare Mobile apps also help doctors remain organized while performing multiple tasks at once.
For example, today oncologists can use separate apps to simultaneously treat patients with different types of cancer.
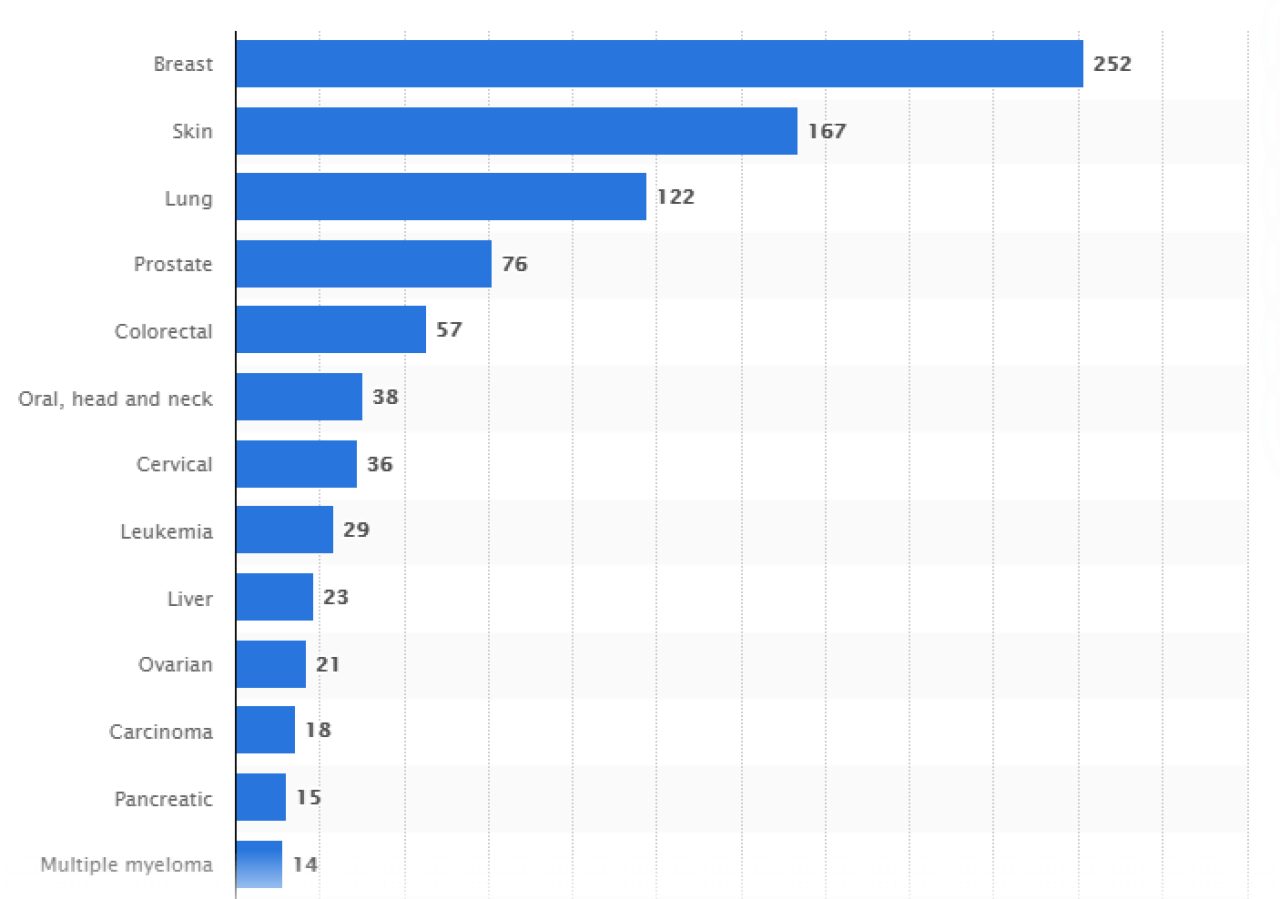
The number of mobile cancer apps available by cancer type as of 2018. (source: statista.com)
Apps may also help reduce stress, making work much easier.
3. Mobile applications simplify communication between doctors and patients.
This seems obvious but is worthy of explicit mention. Applications facilitate distant communication not only within a local area but even between countries.
In many cases, there is no more need to go to the hospital and wait for hours in the emergency room. You can contact a specialist at any time of the day from the comfort of home.
Sometimes, easy and accessible communication with a physician can even save a life.
Imagine that your family doctor has left the country, and you urgently need a prescription for insulin. You can simply contact the specialist, who will write you a prescription online via the app.
Can We Really Trust Healthcare Mobile Apps?
Despite all of their potential benefits, mobile healthcare apps also bring with them certain risks.
Clinical records provided by patients may be not accurate enough.
One of the problems associated with mobile applications is that patients themselves compile information about their previous illnesses and visits to the doctor. Since they are not medical professionals, this information may be inaccurate, or even completely false.
According to Dr. Maureen Baker, Chair of the Royal College of General Practitioners, “Medical histories provided by patients themselves will rarely be as comprehensive as those held by their family doctor. There are also many signs and symptoms that general practitioners look out for when making a diagnosis that the patient might not think to raise.”
The safety and privacy of user data may be at risk.

There are a number of risks associated with medical app security.
First, mobile applications can use third parties to transmit user information whose reliability and privacy protection can never be absolutely assured.
The application itself may contain security holes that attackers can use.
There is also the possibility of the devices physically being compromised. Tony Yang, a post-doctoral researcher at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), said, “Because health apps are mainly used on portable devices such as smartphones and tablets that can easily be stolen, data collected by the apps are particularly at risk.”
Here is a great article by David Pittman, eHealth Reporter at Politico, which includes a detailed analysis of the possible risks related to security in medical mobile apps.
The Future of Mobile Technology in Healthcare
Mobile applications for healthcare are a very promising industry and a place where we can expect increasing infusions of funds.
Take as an example Babylon Health, a typical application used for communication with a physician, which also includes artificial intelligence technology.
Five years ago, 250,000 people were using Babylon Health in the United Kingdom and Ireland, making it very attractive to investors as the app gradually entered other markets.
Eileen Burbidge, American venture capitalist resident and a founding partner at Passion Capital, said, “A company like Babylon Health, by using mobile devices and mobile technology, is hugely interesting because it’s not as capital intensive, you don’t require quite as much investment as a life-sciences business or a pharmaceutical company.”
She also added that investments in med-tech and healthcare are very important to her and her colleagues. After all, the potential market in these areas is the entire world, so recent research is quite optimistic about the future of mobile healthcare technology.
According to the recent research report by Global Market Insights, the mHealth market size is set to exceed USD 289.4 billion by 2025.
Data from the study by Centre for Research in Evidence-Based Practice, Bond University, also show that many doctors use healthcare mobile apps in their practice:
- About two-thirds of the respondents used health apps themselves.
- A little over half of the respondents recommended apps for patients daily (13%), weekly (26%), or monthly (13%).
Some Final Thoughts
Since this field is growing so rapidly, it will take some time until we can definitively assess the impact of mobile technology on the healthcare industry. However, some trends are already becoming clear, which we can summarize as follows:
- The smartphone and healthcare spheres are growing closer to each other. Revenue for applications related to health services is constantly growing.
- Consumers, doctors, and enterprises are interested in medical mobile apps.
- There are many types of healthcare mobile apps, which can be divided into three categories based on their intended audience.
- Applications in the healthcare industry offer many advantages, but also bring with them certain risks.
- Mobile applications for healthcare represent a very promising industry, where future investments are likely.
- Doctors and patients are optimistic about the future of mobile in healthcare.




