Best Practices for Successful Medical Software Development

The COVID-19 pandemic has triggered a wave of digitalization in medicine. In the years ahead, the use of advanced technologies will revolutionize routine diagnostic and treatment approaches, as well as having a positive effect on physician-patient interactions.
Healthcare software enables you to:
-
- Improve health data gathering
- Provide timely care regardless of location
- Reduce medical errors
- Decrease expenses for both hospitals and patients
- Improve communication between physicians and patients
- Increase customer loyalty and engagement
- Provide time-saving features for medical staff
If you’re reading this article, you’re most likely looking for the best practice for building medical software. Well, in this article, we will cover all the ins and outs of medical software development.
Here’s What We’ll Cover
Healthcare Industry Facts & Figures
In 2020, the mHealth market size was valued at over $45B. But the COVID-19 outbreak triggered a drastic surge in market value, and it’s now projected to reach nearly $100B by the end of 2021.
In addition to the doubled market size, overall app usage has also increased greatly. Since the start of the lockdown, the number of healthcare app downloads has increased by 60% worldwide. There are 48,000 healthcare apps available in the App Store and around 47,000 in the Play Store.
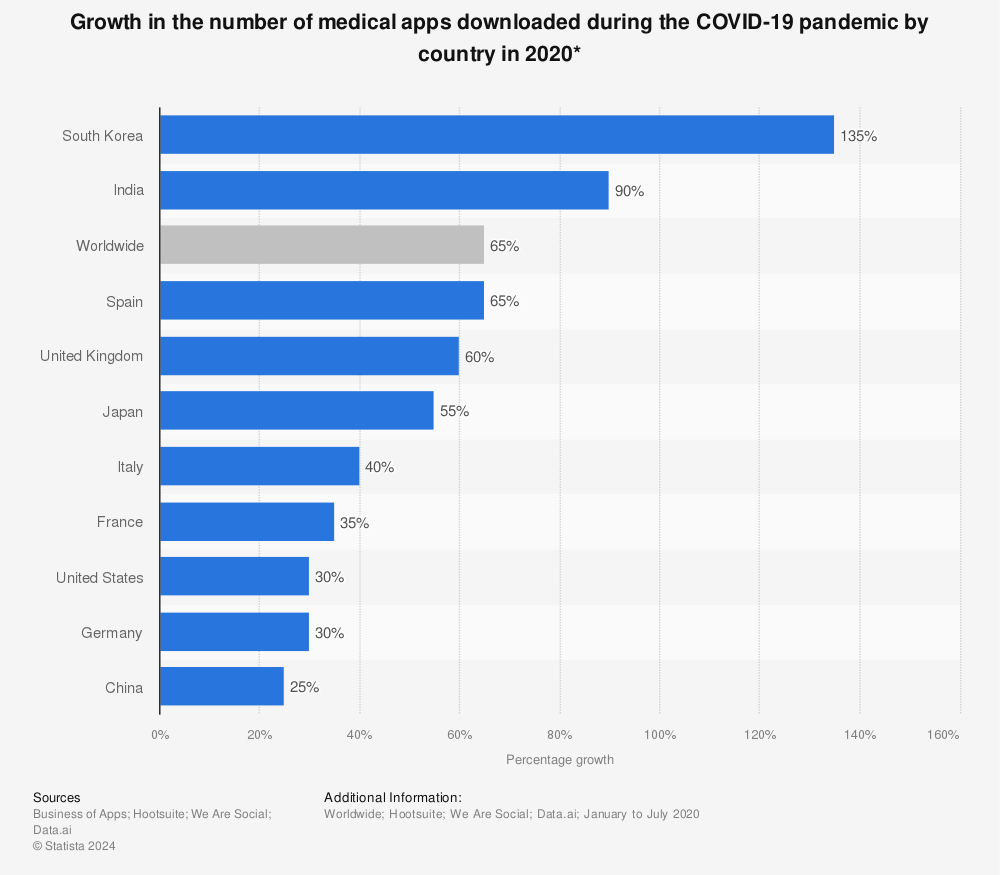
Find more statistics at Statista
The popularity of digital health is driving many startups to try their best in the healthcare industry.
Why Should You Build Custom Medical Software?
Benefits for Clinical Specialists
Digital healthcare solutions enable clinical specialists to reduce paperwork, serve more patients, and access medical data stored in different digital systems via a single convenient interface. Below are several more reasons why medical consultants and healthcare providers prefer healthcare software.
- Additional revenue stream. Clinical specialists find that telemedicine increases their income as it allows them to provide care to more patients.
- Reduced exposure to illness and infection. When providers see patients remotely, they do not have to worry about exposure to any pathogens the patient may carry.
- Patient satisfaction. When a patient does not have to travel to the office or wait for care, they may be more satisfied with their physician.
- Eliminating daily routine paperwork. Keeping all daily doctor–patient interactions documented in an electronic health record (EHR) reduces the burden of routine paperwork.
- Better patient care. EHRs allow physicians to share vital patient data. When all physicians have the same information, they can improve the quality of care and avoid medical errors like prescribing contraindicated medications.
- Reliability. Medical software like EHR has backups in case of any system failures, which means that all files can be restored.
- Reduction of possible mistakes. Digital information is always easy to read, unlike handwritten data, which is often unclear. In other words, an attending physician won’t be confused by prescriptions written by the previous specialist.
- Saving time. A patient’s treatment and disease history is stored in one file, so physicians don’t have to waste time searching for a proper record.
- Seamless collaboration. Your team can communicate effectively thanks to information technology, and provide the best possible care for patients.
Benefits for Patients
For people who cannot go to the doctor’s office and those who prefer to stay home, remote care is a convenient option. They can receive detailed medical information, or show the doctor any visible symptoms that require treatment. Patients expect digital health solutions to be modern, convenient, and consistent with their experience in digitalized industries like banking and e-commerce.
Digital medical solutions are popular with patients thanks to the following advantages:
- Seamless face-to-face communication. Conferencing solutions provide a more convenient and personalized experience for patients, physicians, and other healthcare professionals.
- Remote access to lab results and medical history. Electronic personal health records make information accessible anytime via web-enabled devices, such as computers, smartphones, and tablets. Patients can gather and manage all their health data in one easily accessible location.
- Improved patient security. Practice management software lets providers store and capture patient data quickly, securely, and intuitively. Data and information transfers are encrypted to ensure protected health information is shielded from cybercrime.
- Reduced wait times. Practice management software allows practice staff members to operate smoothly and efficiently to reduce patient wait times. It offers the ability to make appointments and fill out documents remotely.
- No transportation time or costs. When you see your doctor on your mobile device or computer, you can save money on gas, parking, and public transportation. Further, you don’t waste time or risk getting stuck in a traffic jam.
- Additional educational information. With easy-to-use solutions, healthcare experts can share information on thousands of educational topics covering conditions, tests, and treatments.
- Enhanced patient satisfaction. The physician’s ability to instantly access patient records and make informed decisions with the benefit of their medical history at his or her fingertips is a key benefit and driver of patient satisfaction. Patients also want to know that their data is secure with a medical practice.
- Reduced risk of contracting a new illness. By staying home, you get the care you need while avoiding the risk of contracting a new illness in a crowded waiting room or passing your illness on to someone else.
Benefits for Health Organizations
Medical software deals with everyday operations and streamlines clinical workflows. It allows you to improve the patient experience and increase efficiency by automating your healthcare processes.
- Easier access to healthcare data. Online data processing allows one to optimize operations within a practice and improve diagnostics.
- Focus on quality care. Automating routine medical processes allows healthcare providers to concentrate on patient care.
- Reduced costs due to the automation of numerous tasks. Increased automation also helps to address staff shortages as it frees up healthcare professionals from repetitive tasks and allows them to focus on patient care instead.
- Reduced overhead expenses. By using telemedicine services, you might incur fewer overhead costs. For example, you might pay less for front desk support or be able to invest in an office space with fewer exam rooms.
- Increased patient satisfaction and engagement. Due to standardized workflows and automated features, medical providers can work more effectively, which in turn improves patient satisfaction.
- Regular updates. Electronic charts are always updated according to the preventive care guidelines they are connected with. Moreover, all updates are instantaneous and users will receive a notification once an update happens.
- Reliable communication tools. EHRs are easy to access from anywhere in the world. As they have backups, all files can be restored, and it’s hardly possible to lose them.
- Enhanced quality of medical services. Digital information is always easy to read, unlike handwritten data, which is often unclear. Thus, an attending physician won’t be confused by prescriptions written by the previous specialist.
Types of Medical Software
In this section, we will cover the most popular types of healthcare software that are currently used by medical industries. These include:
- Electronic Health Record (EHR) Software
- Electronic Medical Record (EMR)
- Medical Diagnosis Software
- Imaging and Visualization
- Medical Database Software
- E-prescribing Software
- Appointment Scheduling
- Medical Equipment Management
- Hospital Management Software
- Medical Billing
- Medical Research
- Patient Portals
- Health Mobile Apps
Electronic Health Record (EHR) Software
An EHR or electronic health record system is a digital version of a patient’s paper chart. This system allows one to gather in digital format all the patient’s clinical data, including personal information, medical charts, and medicines.
All the patient’s records are portable and easily accessible within a secure platform. A physician can quickly check and analyze previous patient examinations and laboratory tests, and thus provide better diagnosis and treatment. The system can also provide reminders when preventive procedures are due.
EHR serves not only as an organizational tool but also as a full network of practitioners providing a faster and more reliable service than ever before.
Electronic Medical Record (EMR)
An EMR or electronic medical record is the most common type of EHR software. This system also involves information about medications, procedures, and the general course of the patient’s recovery. Physicians can create one EMR for one practice describing individual diseases.
But it should be noted that EMR serves as a digital journal of a single practice, so it’s not convenient to use EMR if other physicians need to observe the patient.
Medical Diagnosis Software
Medical diagnosis software is an intelligent system powered with AI to handle the medical diagnostic process while ensuring precision. This software enables the automated real-time exchange of information among different medical specialties.
For example, a cardiologist might share a diagnosis of a patient based on cardiovascular manifestations. A nephrologist could simultaneously enter data and possible diagnoses based on the patient’s kidney findings. Hence, this system fosters collaboration among different medical fields.
Data Visualization Software
Data visualization software simplifies complex information and converts it into a graphical format that is easier to understand. Health information technology enables clinicians to evaluate the different systems of the body in real-time and make more accurate diagnoses.
For example, the microarray analysis platform, designed by VironIT, aims to perform the complete analysis of gene expression microarray data. Microarray analysis is a high-throughput method that has been widely used to profile gene expression. DNA microarrays are assayed for quantifying amounts of mRNA transcripts present in a sample from which RNA is extracted and the mRNA is isolated. The mRNA transcripts are quantified and the number of mRNA molecules derived from a transcription of a given gene is an approximate estimate of the level of expression of that gene.
Another example is US startup HeartFlow, which invented an app helping to plan heart surgeries. It creates models based on each patient’s diagnosis and enables doctors to plan multiple treatment strategies before the operation even starts.
Medical Database Software
Medical database software enables health professionals to enter patient data like medical history, medications, procedures, and treatment course into a digital platform.
But unlike EHRs, in medical databases, cases are classified according to disease diagnosis. So, there are medical databases specific to coronary heart disease, diabetes, pneumonia, and so on.
E-prescribing Software
E-prescribing software allows physicians to communicate directly with pharmacies regarding prescriptions. This software has been used by hospitals to increase efficiency in providing medications and limiting medication errors to improve patient safety.
Appointment Scheduling
The online appointment scheduling system allows healthcare facilities to maximize the efficiency of the staff and minimize the waiting time of patients. This system enables patients to register by logging in to the online platform, where they are given an appointment number and schedule. Moreover, they can check the availability of a physician, and can cancel or reschedule the appointment. Patients do not have to stand in line at hospitals, which reduces crowding, improves the hospital atmosphere, and increases staff and patient satisfaction.
For instance, in the Zocdoc app, users can look for a top-rated doctor in their area on-demand. The app allows users to make appointments, visit doctors, and video call them.
Medical Equipment Management
Medical equipment management software aims to track and monitor the functionality and maintenance of medical devices. Through this system, medical equipment downtime is reduced.
For example, nurses in the US waste 6,000 hours each month tracking down lost medical equipment. If a nurse needs to use a medical device, they can either spend time wandering the premises looking for it or consult a spreadsheet.
Mymediset SAP add-on software will help one manage medical equipment, loan kits, field and consignment inventory efficiently.
Hospital Management Software
A hospital management software enables scores of high-quality administrative services like management of patient data, medication, and other documents. For instance, some software could be integrated to monitor the workflow of medical professionals. Other programs are designed to assist in financial and administrative functions.
Using this type of healthcare software, you can streamline hospital operations, improve administration and control, enhance patient care, and increase profitability for the stockholders.
For instance, the eHospital hospital management system allows you to manage all hospital operations such as medical, organizational, financial, legal, and corresponding service processing.
Medical Billing
US hospitals use medical billing software for everything from medical billing to best practices for patient care, health institutions, and private practice.
Through the integration of the electronic billing system with EHR, billing records can be correlated and checked with patient medical records. Transactions and medical procedures can be monitored and analyzed to prevent fraud and unnecessary treatments and procedures. There are three basic types of systems: closed, open, and isolated.
Medical Research
Digital health research plays a crucial role in telemedicine and e-health, and it can be defined as medical treatment and research delivered by technology. This is not only data collection, remote observation, and increased mobility. Digital health research empowers patients, provides personalized care, and benefits connected care pathways.
For example, digital platforms designed for medical research could be a repository of medical journals or integrated with EHRs.
Patient Portals
A patient portal is a secure online website that is connected to the EHR, and centrally focused on patient access to health data. These tools offer patients a window into various data points, including lab results, physician notes, their health histories, discharge summaries, and immunizations.
Most portals include features such as direct secure messaging, online appointment scheduling, online bill payments, prescription refill requests, and sometimes even data update capabilities.
For example, the WebMD healthcare app allows users to check their symptoms, get info about drugs, look for diagnoses, and possible treatments.
Health Mobile Apps
There are more than 95,000 healthcare apps available on the App Store and Google Play. They can be split into two categories: apps for professionals and apps for patients. Each category has its own types of apps, depending on their functions and target audience. For example, there are women’s health apps, programs that remind users to take pills, and others that facilitate adherence to rehabilitation plans.
How to Develop Medical Software and Avoid Potential Pitfalls
Before you start to develop medical software, you should decide what kind of software you want, who’ll use it, what problems it’ll solve and how.
If you want to build an EHR system, hospital management software, or other digital solution for a health organization, there are many ways to do it. But we suggest starting with these options:
- Use a ready-made solution. The only thing you have to pay is a monthly subscription fee. But its drawbacks are limited customization and lack of additional features. It also becomes inaccessible if you stop the monthly payments.
- Customize a clone script. If you use a clone, you don’t have to think up new features because they are already in the clone script. But note that you will need to hire a developer to customize and upload it to the app store—which can take a long time and come at an extra cost.
- Develop a custom software. If you decide to build custom medical software from scratch, you will build an iterative and responsive solution with a team of professionals. A custom software solution will be maintained for as long as you need it to be. You will have full access to a technical support team that was involved in the development process. Also, you can rebuild your entire software, or parts of it, if necessary. Custom development will cost you extra, but this approach to the problem has no other drawbacks.
This way, you can get your app in front of the right people fast. Let’s take a brief look at some basic steps that should be taken to create a customized healthcare project.
How to Start: Formulate Your Idea and Your Needs
Identify a problem you want to solve with your software. You should carefully study the most popular competitors and come up with a solution that’ll make you stand out among them.
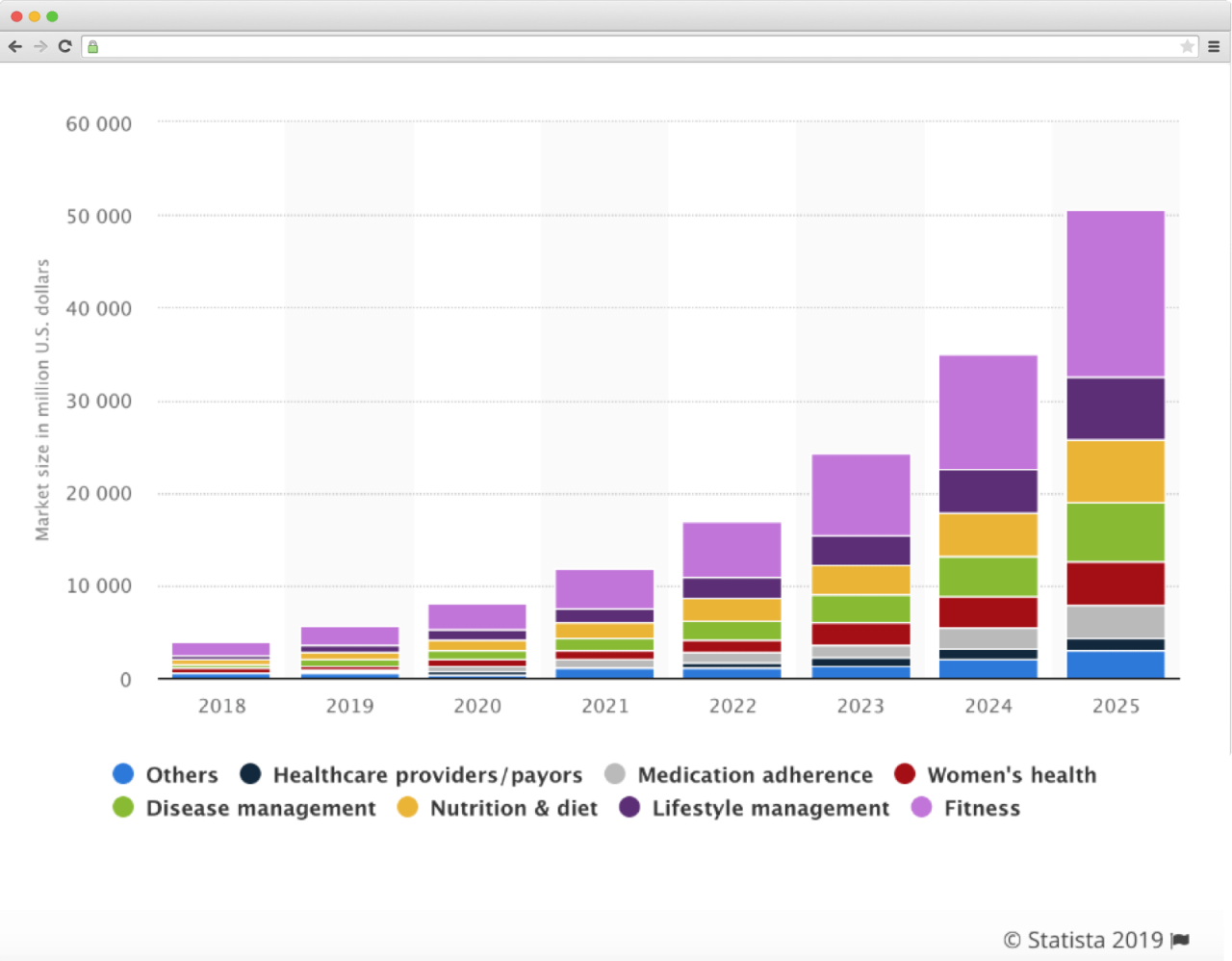
Market share of different healthcare apps in the United States from 2018 to 2025 (in million U.S. dollars)
Know Your Target Audience
The target audience is a whole market segmented by many factors such as country of residence, age, education, average income, and much more. You don’t want to address the wrong audience, so study and divide your target users carefully before getting into the development of the health app.
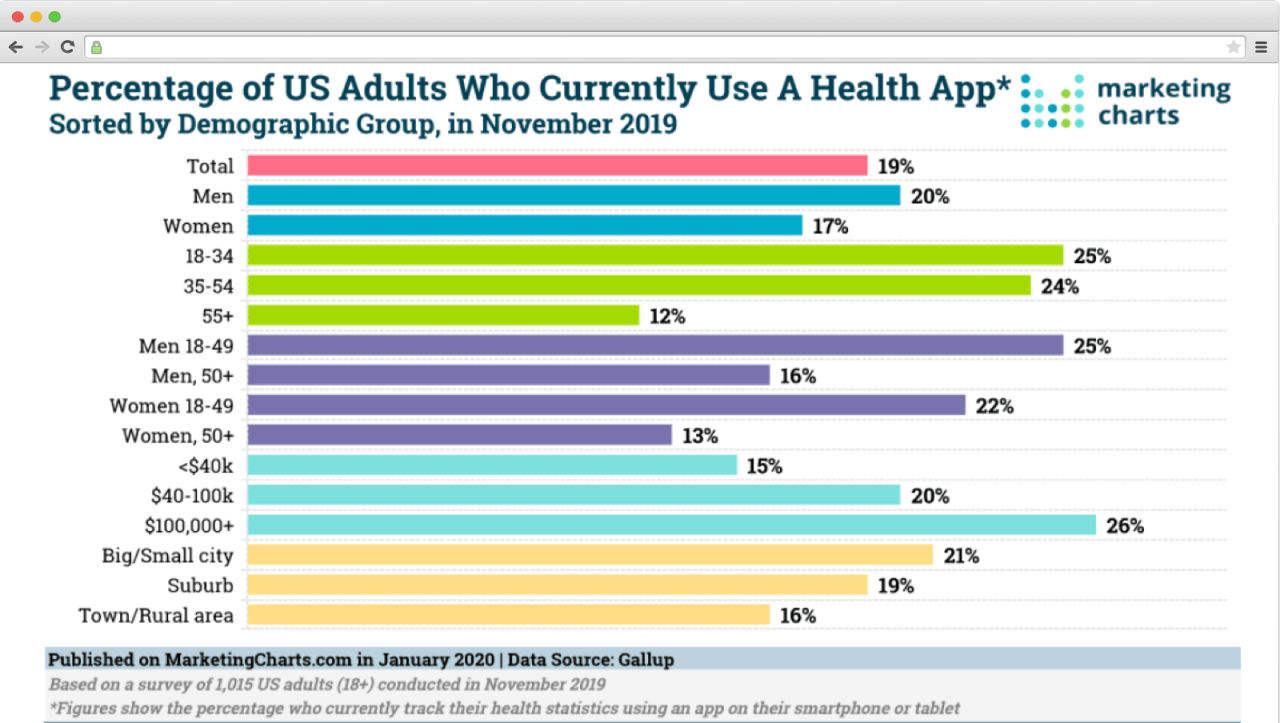
mHealth apps adoption by different criteria (Source Marketing Charts)
Define Functional and Non-functional Requirements
Clear functional and non-functional requirements allow you to reduce development costs and save time.
In a nutshell, the functional requirements drive the application architecture of a system, while the non-functional requirements drive the technical architecture of a system. This means that functional requirements include all the features of your future project and the ways users will engage with it. Non-functional requirements, however, describe how the system works.
Pay Attention to Medical UI/UX Design
A good medical app should be easy to use and navigate. At the UI/UX design stage, you should adhere to some rules to make the design attractive and user-friendly.
For example, older people prefer larger fonts, minimal animations, and easy layout. However, millennials enjoy customizing options, bright colors, and smooth animations.
Choose a Monetization Model
Note that you don’t have to make your app a paid one to generate revenue. To make a profit, you should choose a monetization model for the eHealth solution. Let’s look at some basic monetization methods:
- In-app ads. Advertising is a core money generator. Apps generate money by selling space for ads to third-party companies.
- Freemium. Basic functionality is always free of charge, unless you want to use additional features that are not free.
- Subscription. Users pay a certain fee to use the app for a week or a month or some other period of time.
- Paid. Users can buy an app with a one-time payment.
Provide Data Protection
Healthcare is one of the most regulated industries. Different countries have varying regulations that you should know about and take into consideration before building medical software.
Regulation and compliance in Medical Software Development
- HIPAA. Apps developed for the US market that process, record, and store data must adhere to HIPAA regulations. These rules ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of health information.
- CCPA. This law involves informing the client about what data is being collected, preparing a free report on the collected data if requested by the client, deleting the collected data if requested by the client, and much more.
- GDPR. All healthcare apps operating in the EU must comply with these personal data protection rules. It is important to note that the GDPR applies to both the company that processes data and the company that collects it.
- NIST. This is a collection of standards, tools, and technologies designed to protect the data of users of medical applications in the United States.
- HiTECH. These regulations focus more on the data security of EHR systems, and are also valid in the US. Note that HIPAA-compliant apps are equivalent to HiTECH compliant.
- PIPEDA. Applications working in the Canadian market that store and process personal data must comply with PIPEDA.
Build a Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
Building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is crucial when you are developing an app for the healthcare industry. An MVP includes only essential features and helps to prevent you from overspending. This is the best way to collect feedback from users and find out what they think about your project.
Collect Feedback and Update the Medical Software
After your MVP has been released, you should collect and analyze user feedback. The audience’s opinion can fuel your ideas for future updates. In other words, you can support the app by expanding its functionality and implementing various quality-of-life improvements.
Our Experience of Medical Software Development
Being experienced in developing medical software, we help hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare providers automate their day-to-day processes to improve patient care, data confidentiality, inventory management, and diagnostics.
Below we’d like to show you some eHealth projects we’ve built so far. If you’re interested in seeing more, check out our healthcare projects page.
Medical Services App
This telemedicine solution enables the patient to see a doctor without leaving home or waiting in queues, which can be not only tiresome but also dangerous during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Telemedicine App
This HIPAA-compliant telemedicine app allows patients to ask questions to physicians and share photos or videos of their problems with the entire team of healthcare professionals.
Digital Treatment Assistant
This dedicated customer service platform is designed to help the pharmaceutical industry to fill knowledge gaps and deliver medical support and education directly to physicians.







yuliia says:
This is very useful! Thanks